Sustainability Strategy
Helping to Solve Social Issues through Businesses Focused on Five Material Issues
The future is difficult to predict in a complex world characterized by population growth, developed countries with declining birthrates and aging populations, rapid digital transformation, increasing use of biotechnology, multipolarity in international relations, and a worsening climate crisis. Given the uncertain future the world faces, Konica Minolta has decided to identify the social and environmental issues it must help address. While reaffirming its corporate DNA, the company clarified issues to be addressed by 2030, and then backcasted from that year to determine the targets it must tackle immediately.
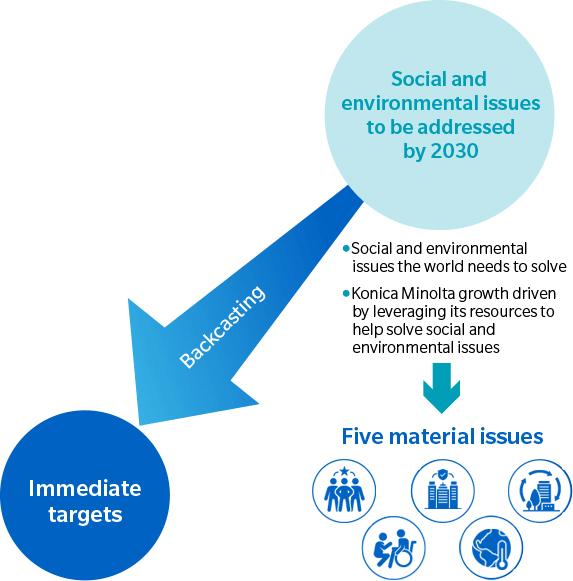
After gaining insight into social and environmental issues expected to be critical by 2030 by examining the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and macro trends, Konica Minolta conducted a materiality analysis from the perspectives of social issues that must be resolved and Konica Minolta's business growth. This led to the identification of five material issues for Konica Minolta to tackle starting in 2020. For each of these issues, a vision was also established, thereby clarifying Konica Minolta's medium and long-term directions for value creation.
Vision for 2030 and Five Material Issue
These five material issues are linked to Konica Minolta’s business growth strategy and are the basis for promoting each business activity. Konica Minolta will pursue initiatives that integrate business growth and social sustainability to create customer and social value that align with the value creation process.
Value Creation Process
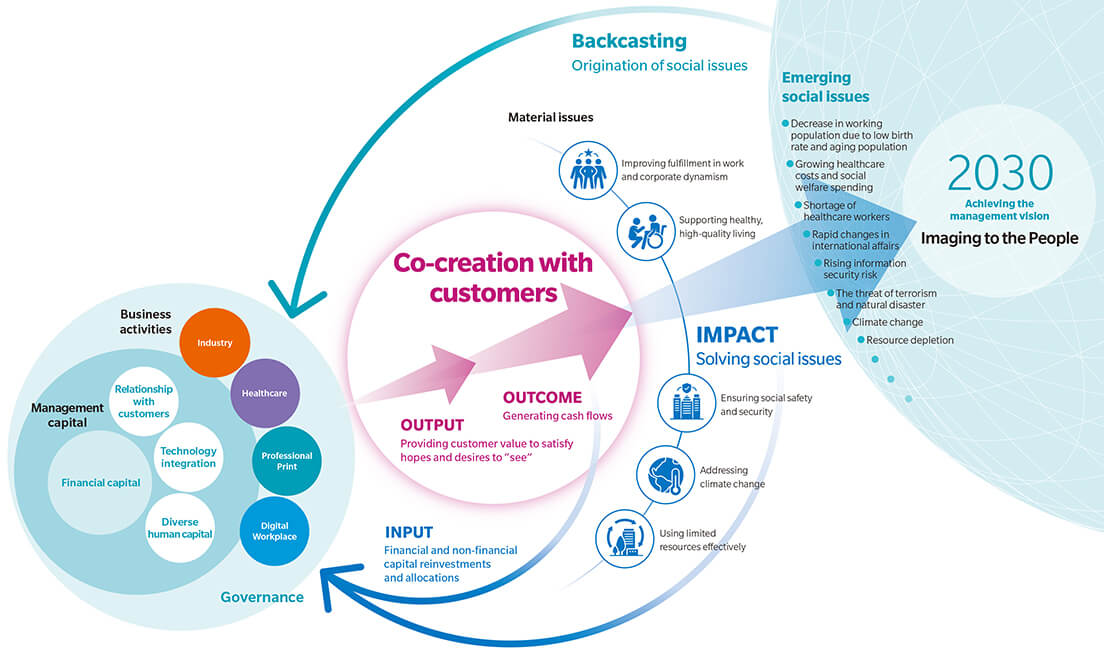
Backcasting from social issues envisioned for 2030, Konica Minolta meets the client’s needs through products and solutions from its four business. Not only by leveraging its strengths in intangible assets (customer relationships, fusion of technologies, and diverse human resources), Konica Minolta also seeks to create customer value through co-creation with customers. At the same time, the Company will continuously repeat this process of generating cash flow, which is the resulting economic value, and expand the impact of solutions for social and environmental issues.
Click below for details on the material issue identification process.
Sustainable Products that Create Customer Value and Social Value
Identifying products and solutions that solve social and environmental issues by material issues.
Opportunities and Risks for Material Issues
Risk Management
Sustainability-related risks (such as climate change, information security, etc.) based on identified material issues are integrated with company-wide risks and managed by the Risk Management Committee.
Opportunities and Risks
The material issues and the related opportunities and risks are shown in the table below. Each of Konica Minolta’s businesses works to create value with an awareness of material issues. For example, in the Industry Business, Konica Minolta is working to resolve the issue of passing on the skills of top workers by automating the inspection process, which relies on the skills of experienced workers at production sites, and to reduce the number of required workers, and contribute to greater quality of end products, and improve fulfillment in work and corporate dynamism. In the professional print business, the Company is helping to address climate change and use limited resources effectively by transforming its customers' supply chains to reduce transport, storage, disposal, and intermediate materials through production conducted with the right timing, quantities, and location. Furthermore, in the healthcare business, we contribute to "supporting healthy, high-quality living" by realizing early detection and diagnosis.
| Social and environmental issues (Assumptions for 2030) |
Opportunities | Risks | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Improving fulfillment in work and corporate dynamism | Bridging the digital divide and eliminating the labor shortage Opportunity gaps for employment and creation |
Transforming workflow and supply chain to help customers improve productivity and shift to more creative work | Declining employee diversity, independence, and ability to innovate due to stagnant efforts to create workplaces that promote diversity |
| Supporting healthy, high-quality living | Lower sustainability of medical and nursing care Restricted medical care access Reduced social security spending |
Contributing to early diagnosis, lower medical costs, and higher QOL through imaging and medical IT services | |
| Ensuring social safety and security | Risk of workplace accidents due to aging facilities, etc. | Ensuring the safety and security of businesses and society through image monitoring Ensuring customer quality through advanced measurement and inspection |
Damage to company or society due to serious accidents caused by products or services |
| Addressing climate change | Adaptation to changes associated with the transition to a carbon-neutral world Impact of climate change on society, the economy, and ecosystem |
Reducing the impact of energy and CO2 on client companies and society by transforming the workflow and supply chain | Declining competitiveness due to delayed transition to sustainable energy Delayed business restructuring to accommodate the paperless trend Supply chain disruptions due to abnormal weather |
| Using limited resources effectively | Adaptation to changes associated with the transition to a circular economy Impact of resource depletion on society, the economy, and ecosystem |
Reducing resource use and improving resource efficiency at client companies and in society by transforming the workflow and supply chain | Declining competitiveness due to delayed switching to sustainable raw materials Increasing material costs due to raw material shortages and supply instability |
Impact Assessment on External Stakeholders
| Material Issues | Impact on External Stakeholders | Output | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Addressing Climate Change | If dire climate change predictions materialize, rising sea levels will submerge coastlines and damage biodiversity. There will likely also be frequent severe weather events, such as typhoons and hurricanes, which could have a significant impact on both industry and people's lives. Konica Minolta is promoting the reduction of CO2 emissions by downsizing its products, incorporating energy-saving designs, and implementing energy conservation and renewable energy in production. We believe that these actions will lead to a reduction in the economic losses brought to society and the environment. |
Scope 1,2,3 CO2 reduction: 33,000 t (FY2023) |
Social cost of reduced carbon*1: 950 million yen |
| Using Limited Resources Effectively | In order to make more effective use of finite resources, it is necessary not only to reduce the amount of resources wasted, but also to recover and recycle waste. Konica Minolta has developed a new technology to recycle disposable plastics such as milk bottles and PET bottles. The company is contributing to waste reduction by actively using recycled plastics for the housings and consumables of its MFPs. We believe this will help reduce waste disposal and management costs for society as a whole. |
Amount of recycled plastic introduced: 4,000 t (FY2023) |
Social cost of reduced waste*2: 180 million yen |
Notes:
- *1
- Social cost of carbon is calculated at 190 US dollars per ton of CO2 based on the survey data from the "Report on the Social Cost of Greenhouse Gases" (U.S. EPA, 2022).
- *2
- Social cost of waste is calculated at 46,000 yen per ton of waste based on the waste disposal fee of the Tokyo Metropolitan Government (Tokyo Twenty-three Wards Cleaning Partial Administrative Association).











